What are the different types of Ball Screws?
The JIS standard categorizes Ball Screws into two types: for positioning and for transportation. KURODA categorizes these into precision grades: C0 to C5 for positioning, and C7 and C10 for transportation.
For more information on accuracy, please also see "I want to know about the accuracy grades of Ball Screws."
The standard does not specify any particular manufacturing method, so any manufacturing method is acceptable.
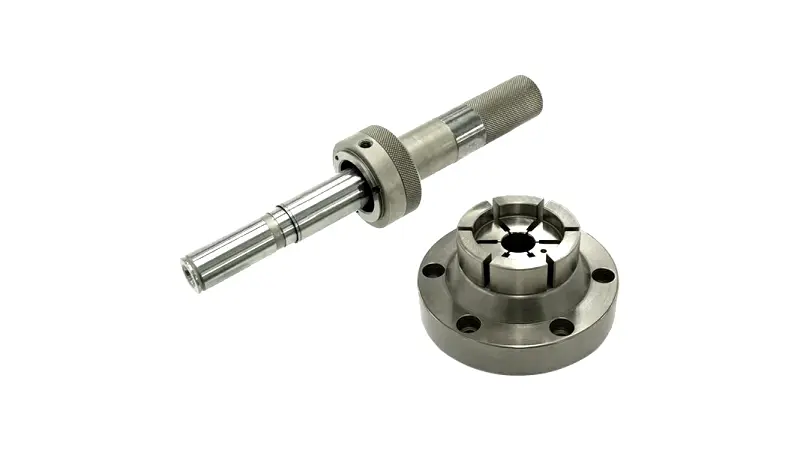
The main components of a ball screw are the screw shaft, nut, steel ball circulation part, and steel balls, but among these, there are two representative types depending on the manufacturing method of the screw shaft: "rolled Ball Screws" and "ground Ball Screws." The characteristics of these two types are explained below.
Rolled Ball Screw
Molding method
The screw shaft of a rolled ball screw is made by forming a screw groove using a tool called a rolling die while rotating a round steel bar.
The rolling die has a screw groove and multiple convex ridges on the outer periphery, and the steel is pressed against a pair of rolling dies to form the screw groove.
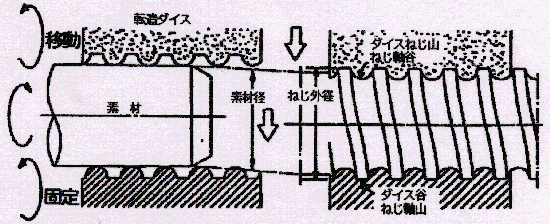
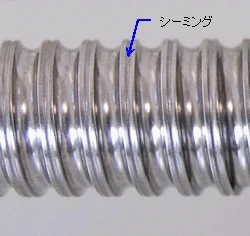
Appearance of the screw shaft
Lines called seaming can be seen on the exterior of the screw shaft. (Some seams are difficult to see depending on the combination of shaft and lead.)
Manufacturing process (outline)
Rolling → Heat treatment → End processing
Lead Accuracy
In order to achieve the target precision through the above-mentioned "rolling -> heat treatment" process, the following precision grades are generally used:
C7 grade, C10 grade
Axial clearance
In rolled products, the cylindricity of the screw shaft is slightly inferior to that of ground products, so good operation may not be obtained with a preloaded product in which the axial clearance is extremely small or set to 0 (zero), so the general axial clearance is set to about 0.03 to 0.20 mm.
Nut combination method
Generally, it is a single nut.
Ground Ball Screw
Molding method
The screw shaft of a ground ball screw is manufactured by cutting a screw groove into a round steel bar using a cutting tool or grinding wheel.
Appearance of the screw shaft
The outer periphery of the screw shaft is machined by cylindrical grinding to give it a smooth appearance.

Manufacturing process (outline)
Shaft exterior shape forming process → Heat treatment → Cylindrical grinding → Thread groove grinding → End processing
Lead Accuracy
Unlike rolled Ball Screws, ground Ball Screws can be manufactured with high and low precision because precision can be achieved in the process after heat treatment.
Class C0, Class C1, *Class C2, Class C3, *Class C4, Class C5, Class C7, Class C10
- Grades marked with an asterisk are KURODA's own standards. Please refer to the catalog for details.
Axial clearance
With ground products, the cylindricity of the screw shaft can be stably manufactured, so it is possible to manufacture preloaded products with axial clearance of 0.005 to 0.20 mm.
Nut combination method
The following grinding products can be manufactured.
- Single Nut
- Double Nut
- Integral Nut
For more information about the above combination methods, "What is the difference between single nuts, double nuts, and integral nuts for Ball Screws?" Please also take a look at the information posted on the website.
Technical information list about Ball Screws
Inquiries About Products
Please contact us using the inquiry form or your nearest sales office.