What is the life of a ballscrew actuator? (1)
electric motor
The movement of the sliding part of a ball screw actuator is a repeated movement within a certain range, left and right when installed horizontally, and up and down when installed vertically, regardless of the application. Therefore, the driving source for the rotating shaft is something that can easily control forward and reverse rotation. In terms of classification of prime movers, fluid machines (air motors, hydraulic motors, etc.) and heat engines (steam engines, Otto engines, etc.) use electric motors that can be controlled with simple circuits, as it is sometimes difficult to switch between forward and reverse rotation.
Generally, servo motors and stepping motors are used as electric motors suitable for this movement.
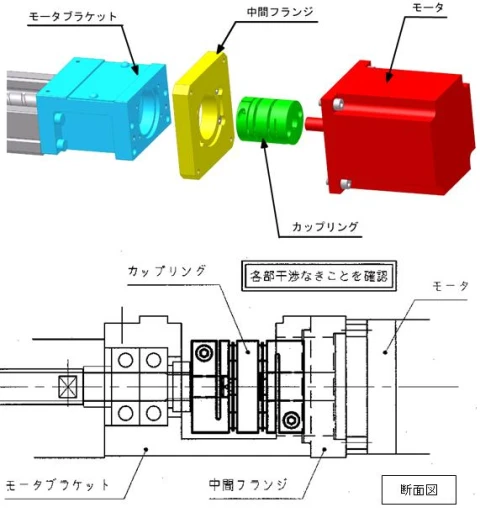
The electric motor and actuator are joined as shown in Figure 1, for example. KURODA offers a wide variety of motor brackets and intermediate flanges so that products from various motor manufacturers can be used.
Please refer to our catalog for details. We are also flexible in responding to requests for products not listed in the catalog, so please do not hesitate to contact us in such cases.
manual
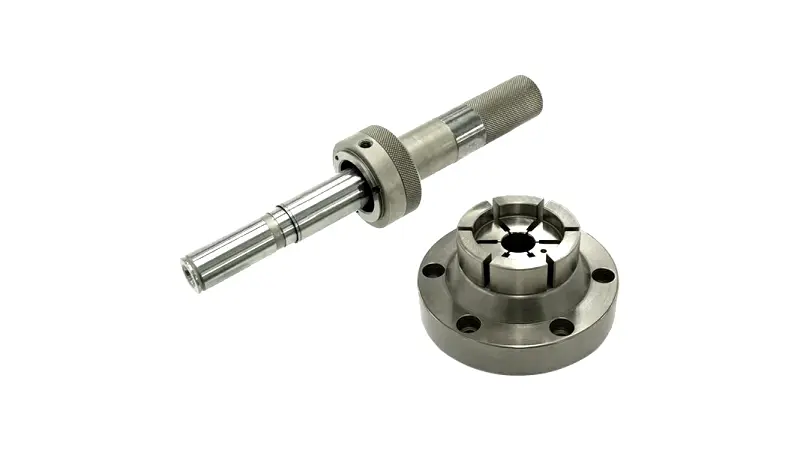
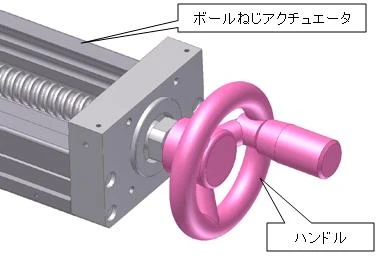
Another way to freely and easily rotate a rotating shaft in both forward and reverse directions other than with an electric motor is by manual drive.
Since an actuator is a mechanism that converts rotary motion into linear motion, it is also possible to drive it manually with the handle shown in Figure 2. When using this, it is also effective to attach a device that can detect position, such as an encoder, to take advantage of the positioning accuracy of the ball screw.
Inquiries About Products
Please contact us using the inquiry form or your nearest sales office.